|
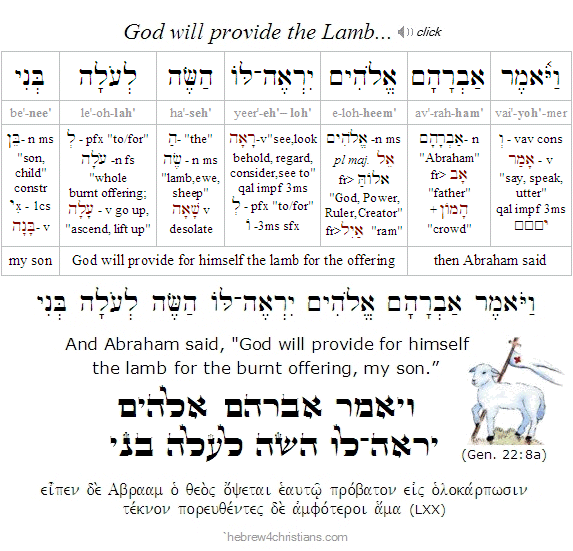
The word "love" (אָהַב) first appears in the Scriptures regarding Abraham's passion for his son: "Take your son, your only son Isaac, whom you love, and go to the land of Moriah, and offer him there as a burnt offering on one of the mountains of which I shall tell you" (Gen. 22:2). After journeying to the place, Abraham bound Isaac, laid him upon an altar, and raised his knife to slay him. At the very last moment, the Angel of the Lord called out: "Abraham! Abraham! Do not lay your hand on the lad or do anything to him, for now I know that you fear God, seeing you have not withheld your son, your only son, from me" (Gen. 22:11-12). Abraham then "lifted up his eyes" and saw a ram "caught in a thicket" which he offered the place of his beloved son. Abraham named the altar Adonai-Yireh, "the LORD who provides" (Gen. 22:14). The sacrifice of the lamb for Isaac portrayed the sacrifice of Yeshua, the great 'Lamb of God' (שֵׂה הָאֱלהִים) who would offer up his life in exchange for the trusting sinner (John 1:29). Indeed the story of how God provided the lamb - both at Moriah and later during the Passover in Egypt - may be understood as the "Gospel according to Moses" (Luke 24:27; John 5:46).
Hebrew Lesson:
Genesis 22:8 Hebrew Reading (click):
Isaac not only pictures the sinner who trusts in God's sacrificial substitute, but also the One who offered himself in obedience to his heavenly Father. The Promised Seed illustrates how Yeshua "humbled himself by becoming obedient to the point of death, even death on a cross" (Phil. 2:7), and in that sense he is a type of Messiah. For instance, both Isaac and Yeshua were born miraculously; both were called "only begotten sons"; both were to be sacrificed by their fathers at Moriah; both experienced a "passion"; both willingly took up the means of his own execution; both were to be resurrected on the third day (Gen. 22:5, Heb. 11:17-19); and both demonstrate that one life can be sacrificed for another – the ram for Isaac, and Yeshua for all of mankind...
The first time the word "Torah" (תּוֹרָה) occurs in the Bible refers to the faith of Abraham (see Gen. 26:5), and the second time refers to the law of Passover: "There shall be one teaching (Torah) for the native and for the stranger" (Exod. 12:49). There is a link here. Abraham lived before the time of the Exodus, of course, and therefore he observed Passover by offering the lamb in place of his son (Gen. 26:5). Abraham revealed that the inner meaning of Torah is that the "righteous shall live by faith" (Hab. 2:4, Rom. 1:17) and that God justifies the sinner who trusts in him (Heb. 11:17-19; Rom. 4:5). During the Exodus from Egypt, Moses declared that the blood of the Passover lamb would be a "sign" of imputed righteousness secured by faith - with no "leaven," or human works, added. This is the "life-for-life" principle that underlies the sacrificial system of the Tabernacle revealed at Sinai as well. Ultimately all true Torah points to Yeshua, the Lamb of God (שֵׂה הָאֱלהִים), who died upon the cross for our offenses and was raised again for our justification (Rom. 4:25).
Hebrew Lesson:
John 1:29b Hebrew Reading (click):
Abraham trusted in God's provision: "God will provide for Himself the Lamb for the burnt offering, my son" (Gen. 22:8). The cross itself speaks to the question of "faith vs. works." At the time of the crucifixion of the Messiah, man was "shut out" because of the darkness and utter sanctity of the sacrifice of Yeshua as the Lamb of God who bore all the sins of the world... At the time of utmost darkness, man was on the "other side of the cloud," put into a "deep sleep" not unlike what Abraham had earlier experienced at the covenant of the parts (Gen. 15:12). Every human being stood helplessly on the other side of the cross; no one else participated to make us right with God: It was all Yeshua and the Father, and the Father and Yeshua alone... In that inner sanctum, that holy of holies, shammah! atonement was made.
|